8. Voltage Sensor¶
There are many applications for the voltage sensor, such as measuring battery levels (Voltage), estimating battery life, tracking solar power generation or even to measure how many power consumption is being used by the raspberry pi. This module allows you to measure voltages of 0-25V.
Warning
Before proceeding with this sensor, you will need to learn about the MCP3008 ADC.
8.1. Connecting the Sensor¶
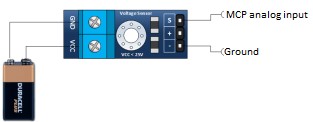
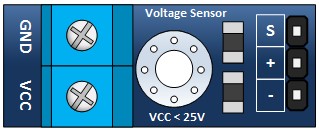
Inputs:
- GND: Connected to the low side of the voltage you are measuring.
- VCC: Connected to the high side of the voltage you are measuring
Outputs
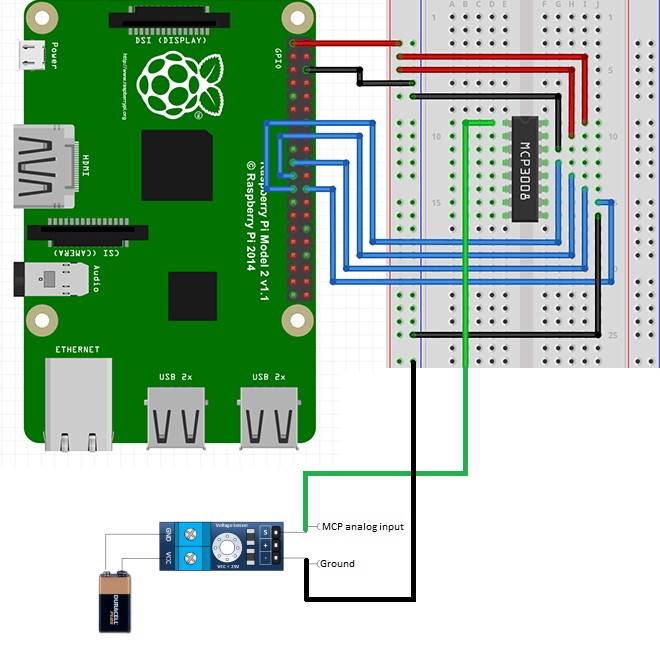
- S: Connected to your MCP analog input.
- ‘-‘ (or minus): Connected to the ground.
- ‘+’: not connected.
Note that the voltage sensor is an analog sensor and cannot be connected directly to the Raspberry Pi pins. It needs an analog to digital converter, MCP3008 in this case, in order to collect proper data.
Full circuit:
8.2. Python Program to Read Voltage¶