2. Passive Components¶
2.1. Resistor¶
Resistors are electric components that have a constant electrical resistance. The electrical resistance of a resistor is measured in ohms and its symbol is the greek letter ‘Ω’(omega). Resistors come in different sizes depending on the function they are needed for, the main use of resistors is to lower the current and protect electronic components from burning out.

To identify the size of the resistor, you can use the color bands found on each individual resistor: The first two bands indicate the two most-significant digits of the resistor’s value. The third band is a weight value, which multiplies the two significant digits by a power of ten.
Note
An easier alternative to memorizing the color codes and performing calculations is to use an application for determining resistance values:
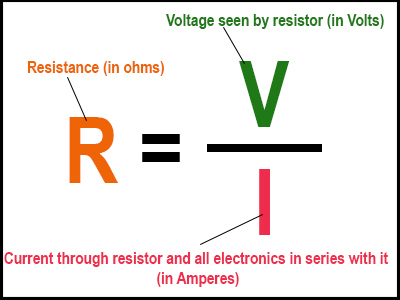
In order to find the resistor value we need to limit a certain voltage to a certain current, we can use Ohm’s Law:
2.2. Diode¶
Diodes are components that only allow current to flow in one direction and block any current from flowing in the opposite direction.

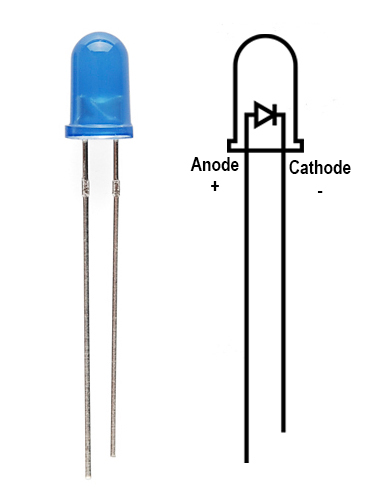
To be more precise, the diode is made up of a cathode and an anode, and current can only flow from the anode to the cathode!
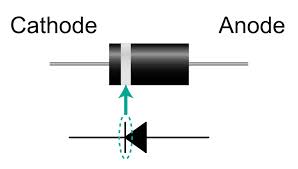
We can distinguish the anode from the cathode by the white mark on the diode:
Diodes will mostly be used to protect the Pi and other electronic components from reverse current such as the one that a motor generates when it turns.
Keep in mind that there exists many variations of diodes. A very interesting variation is the LED (Light Emitting Diode) which, on top of being a diode also generates light when current is passes through it!